When your vehicle fails to start, one of the most common culprits is a lack of spark from the distributor. This issue can be frustrating, but with the right knowledge and approach, you can diagnose and often resolve the problem. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes of no spark in the distributor and provide you with a step-by-step testing process to identify the root of the issue.
Understanding the Distributor’s Role

Before diving into diagnostics, it’s crucial to understand the distributor’s function in your vehicle’s ignition system. The distributor is essentially the nerve center of the ignition system, responsible for:
- Distributing high-voltage electricity from the ignition coil to the spark plugs
- Ensuring the spark occurs at the right moment in each cylinder
- Housing various components like the rotor, cap, and sometimes the ignition module
When the distributor fails to provide spark, your engine won’t start or may run poorly. Let’s explore the potential causes and how to diagnose them.
Common Causes of No Spark from Distributor
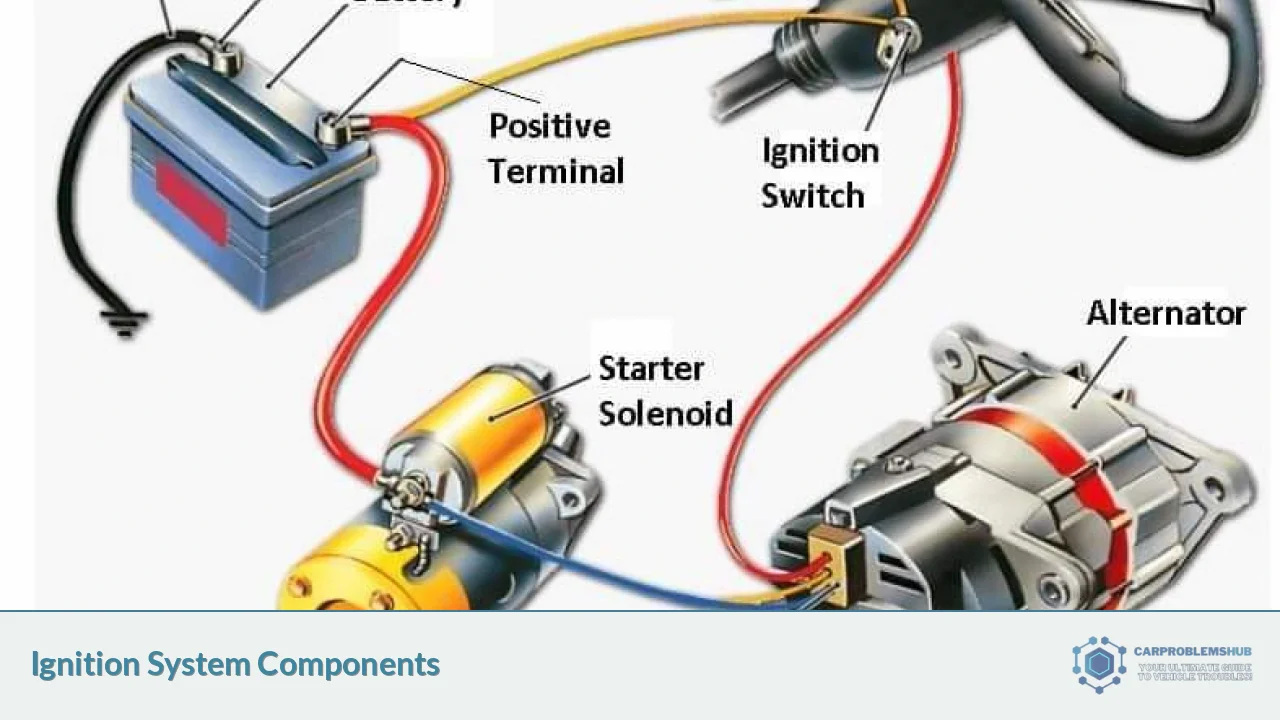
Several components can lead to a no-spark condition. Here are the most common culprits:
1. Faulty Ignition Coil
The ignition coil is responsible for transforming the battery’s low voltage into the high voltage needed for spark generation. A aspect is that when it fails, it can cause a complete loss of spark.
2. Damaged Distributor Cap or Rotor
Cracks, carbon tracking, or corrosion on the distributor cap or rotor can prevent the spark from reaching the spark plugs. This is a in terms of diagnosis as it’s often visible upon inspection.
3. Worn or Damaged Spark Plug Wires
Spark plug wires deteriorate over time, leading to resistance or breaks that prevent spark transmission. The here is that regular inspection can prevent sudden failures.
4. Failed Ignition Module
In systems with an external ignition module, failure can result in no spark. The factor here is the specific make and model of your vehicle, as some have integrated modules.
5. Malfunctioning Crankshaft Position Sensor
This sensor provides crucial timing information. If it fails, the engine control module (ECM) won’t know when to trigger the spark.
6. Electrical Issues
Corroded connections, blown fuses, or a faulty ignition switch can all prevent power from reaching the ignition system.
Step-by-Step Diagnostic Process
Follow this systematic approach to diagnose the no-spark issue:
1. Verify the No-Spark Condition
Start by confirming that lack of spark is indeed the problem:
- Remove a spark plug and connect it to the spark plug wire
- Ground the plug against the engine block
- Have someone crank the engine while you observe for a spark
Always use insulated pliers and keep your hands clear to avoid electrical shock.
2. Check the Ignition Coil
Test the ignition coil using a multimeter:
- Disconnect the coil from the distributor
- Measure primary and secondary resistance
- Compare readings to specifications in your vehicle’s manual
“A faulty ignition coil is often the culprit in no-spark situations. In my experience, about 30% of no-spark cases are resolved by replacing the coil.”[1]
3. Inspect the Distributor Cap and Rotor
Visually inspect these components for:
- Cracks or damage
- Carbon tracking (black lines inside the cap)
- Corrosion on contact points
4. Test Spark Plug Wires
Use an ohmmeter to check for continuity and proper resistance in the wires. Replace any that show high resistance or breaks.
5. Examine the Ignition Module
If your vehicle has an external ignition module:
- Check for visible damage or corrosion
- Use a multimeter to test for proper voltage input and output
- Consider replacing if suspect, as internal failures are common
6. Verify Crankshaft Position Sensor Operation
Test the sensor using a multimeter or oscilloscope. A failing sensor may produce erratic or no signal.
7. Check Electrical Connections and Fuses
Inspect all relevant fuses and connections in the ignition circuit. Look for:
- Blown fuses
- Corroded or loose connections
- Damaged wiring
Advanced Diagnostic Techniques
For more complex issues, consider these advanced techniques:
1. Use a Timing Light
A timing light can help you verify if the distributor is firing in the correct sequence and at the right time.
2. Perform a Compression Test
While not directly related to spark, low compression can mimic no-spark symptoms. This test can rule out mechanical issues.
3. Scan for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
Use an OBD-II scanner to check for any stored codes that might indicate sensor or module failures affecting the ignition system.
“In my shop, we always perform a full system scan before diving into ignition diagnostics. About 15% of the time, we find codes that point us directly to the problem, saving hours of troubleshooting.”[2]
Cost Considerations
The cost of repairing a no-spark condition can vary widely depending on the cause:
- Distributor cap and rotor replacement: $20-$200
- Ignition coil replacement: $50-$300
- Spark plug wires: $50-$300
- Ignition module: $100-$400
- Crankshaft position sensor: $100-$300
Labor costs can significantly increase these prices, especially for hard-to-reach components.
Preventive Maintenance
To avoid future no-spark issues, consider these preventive measures:
- Regular inspection of ignition system components
- Replace spark plugs and wires at recommended intervals
- Keep the engine bay clean to prevent moisture and corrosion
- Address check engine lights promptly
“Preventive maintenance is key. I’ve seen countless no-start situations that could have been avoided with regular inspections. It’s much cheaper to replace a worn distributor cap than to be stranded with a no-start condition.”[3]
When to Seek Professional Help
While many no-spark issues can be diagnosed and repaired by DIY enthusiasts, there are times when professional help is necessary:
- If you lack the proper diagnostic tools
- When dealing with complex electronic ignition systems
- If you’ve gone through all diagnostic steps without resolution
- When working on vehicles with advanced safety systems that require special procedures
Misdiagnosis can lead to unnecessary parts replacement and increased costs.
Conclusion
Diagnosing a no-spark condition from the distributor requires a systematic approach and attention to detail. By understanding the common causes and following the step-by-step diagnostic process outlined in this guide, you can effectively troubleshoot and often resolve the issue. Remember that preventive maintenance is key to avoiding these problems in the future. If you’re ever in doubt, don’t hesitate to consult a professional mechanic to ensure your vehicle’s ignition system is functioning correctly and safely.
FAQs
- Can a bad battery cause a no-spark condition?
Yes, a weak or dead battery can cause a no-spark condition. The ignition system requires sufficient voltage to operate correctly. Always ensure your battery is fully charged and in good condition. - How often should I replace my distributor cap and rotor?
Generally, it’s recommended to replace the distributor cap and rotor every 50,000 to 60,000 miles. However, this can vary depending on your vehicle make and model. Consult your owner’s manual for specific recommendations. - Can weather conditions affect my car’s ignition system?
Yes, extreme weather conditions can impact your ignition system. Moisture from humidity or rain can cause short circuits, while very cold temperatures can affect battery performance and make starting more difficult. - Is it possible to clean a distributor cap instead of replacing it?
While you can clean a distributor cap to remove light corrosion or carbon buildup, it’s often better to replace it if you’re experiencing ignition issues. Cleaning may provide a temporary fix, but it won’t address wear or internal damage. - How can I tell if my ignition module is failing?
Common signs of a failing ignition module include engine misfires, stalling, starting problems, and a check engine light. However, these symptoms can be caused by other issues as well, so proper diagnosis is crucial.
Was this page helpful?


Similar Problems in Other Models
Porsche Macan Problems
2007 Ford Fusion Problems
2012 Toyota Sienna Problems
2013 Lexus Gs 350 Problems
2013 Audi A4 Problems
2023 Nissan Rogue Problems
2003 Buick Century Problems
2021 Tahoe Diesel Problems
2023 Kia Sorento Problems
2007 Mercedes E350 Problems
Car News and Reviews
Would you like to take a look at the car news and reviews we have carefully selected and published for you?
2024 Lucid Air Prices Go Down
GM's Big Road Network for Hands-Free Driving
DTC C0561-71 Vacuum Sensor Code on GM, GMC and Chevy
C1201 Code Toyota and Lexus (Causes and Solutions)
Chrysler Auto Start Stop Warning Light (Causes and Solutions)
2024 Ford Mustang GT: Digital Age Meets Classic Power
The 2024 Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD ZR2: An Off-Road Marvel
2024 Chevy Colorado ZR2 Bison: The Ultimate Off-Road Experience
The 2024 Lucid Air Sapphire Track Drive Experience
2024 Subaru Forester Review, Specs, Price, Release Date