Drive cycle issues refer to problems that occur during the standardized testing procedure used to evaluate a vehicle’s onboard diagnostic (OBD) system performance. These issues can affect the engine, transmission, and emissions control systems, potentially leading to failed emissions tests, decreased fuel efficiency, and increased maintenance costs. Understanding and diagnosing drive cycle issues is crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance and ensuring compliance with emissions regulations.
Understanding Drive Cycles and Their Importance
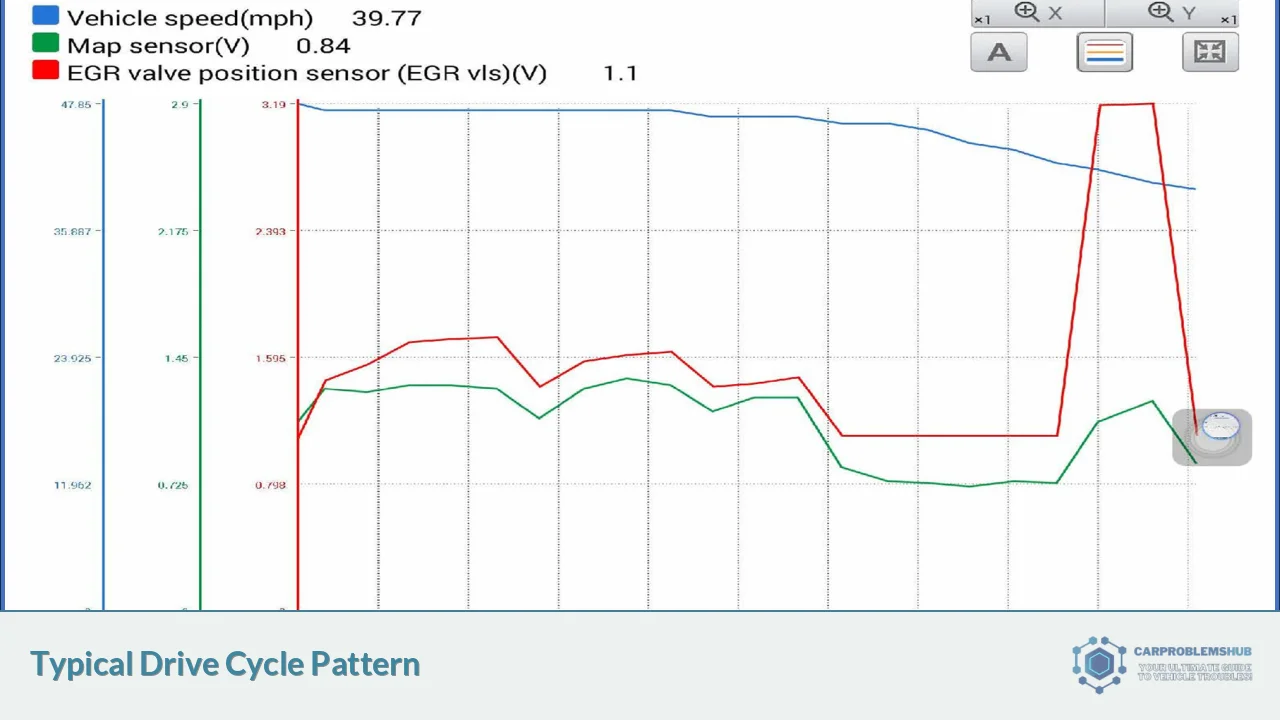
A drive cycle is a specific sequence of driving conditions designed to simulate real-world driving patterns. It typically includes a combination of cold starts, acceleration, steady-speed driving, deceleration, and idling. The purpose of a drive cycle is to:
- Evaluate the performance of the vehicle’s emissions control systems
- Ensure that the vehicle meets regulatory standards for emissions and fuel economy
- Allow the vehicle’s OBD system to run self-tests on various components
- Reset diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and turn off the check engine light after repairs
positive Properly completed drive cycles help maintain optimal vehicle performance, reduce emissions, and prevent potential issues from escalating.
Common Drive Cycle Issues and Their Causes

Drive cycle issues can manifest in various ways and have multiple causes. Here are some of the most common problems:
1. Incomplete Drive Cycles
An incomplete drive cycle occurs when the vehicle’s OBD system fails to run all necessary tests during the prescribed driving sequence. This can happen due to:
- Insufficient driving time or distance
- Improper driving conditions (e.g., not reaching required speeds or engine loads)
- Recent battery disconnection or code clearing
2. Persistent Check Engine Light
If the check engine light remains on after completing a drive cycle, it may indicate:
- Unresolved issues with emissions-related components
- Malfunctioning sensors or actuators
- Problems with the catalytic converter or oxygen sensors
3. Failed Emissions Tests
Failing an emissions test despite completing a drive cycle could be due to:
- Actual emissions-related problems
- Incomplete readiness monitors
- Recent repairs that haven’t been properly verified by the OBD system
4. Inconsistent Monitor Readiness
Some vehicles may struggle to set all readiness monitors, which can be caused by:
- Intermittent sensor issues
- Software glitches in the vehicle’s ECU
- Borderline component performance
Diagnosing Drive Cycle Issues
Proper diagnosis of drive cycle issues requires a systematic approach and often specialized tools. Here’s a step-by-step guide to diagnosing these problems:
1. Preparation
Before attempting to diagnose drive cycle issues, ensure the following conditions are met:
- The fuel tank is between 30% and 70% full[1]
- The battery is in good condition and fully charged
- The vehicle has been parked overnight (or for at least 8 hours) in an environment below 90°F[4]
- All doors are closed, and keys are out of the ignition during the cool-down period[4]
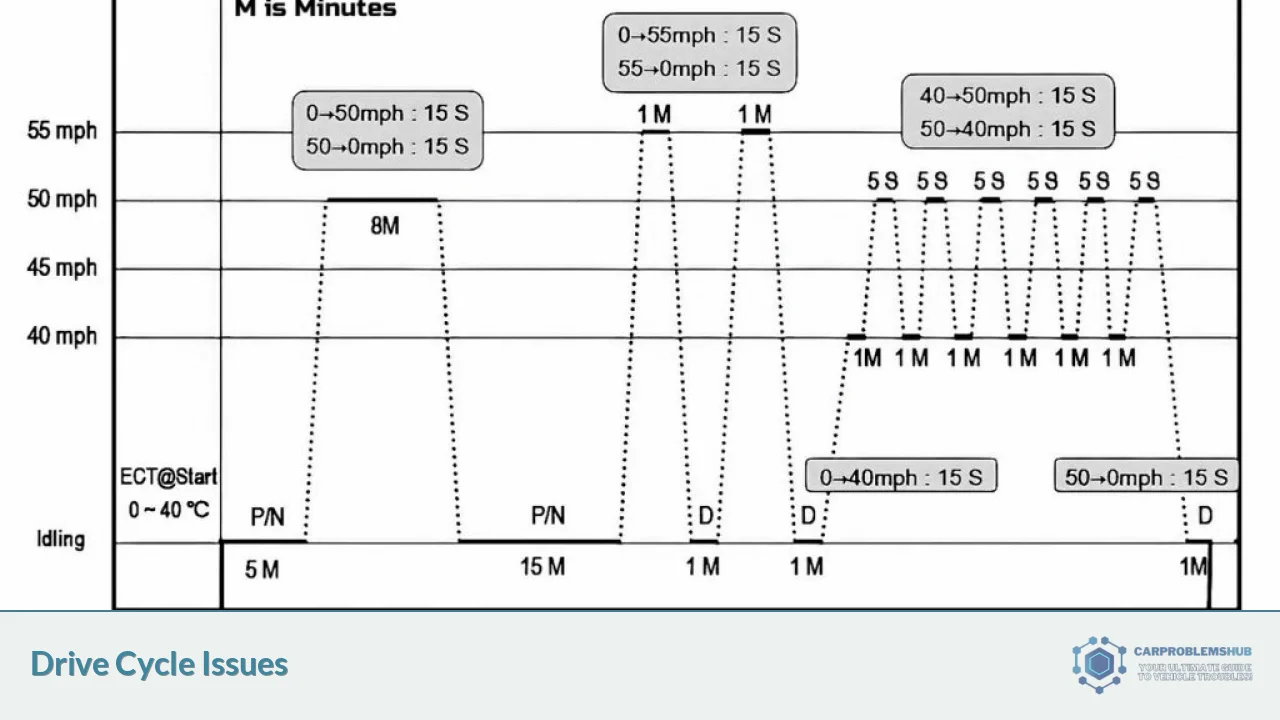
2. Perform a Basic Drive Cycle
Follow these steps to complete a basic drive cycle:
- Start the engine and let it idle for 5 minutes to reach normal operating temperature[2]
- Drive at moderate speeds (40-45 mph) for 5-10 minutes[2]
- Maintain a steady speed of 50-55 mph for 10-15 minutes[2]
- Decelerate to 30-35 mph without braking and maintain for 5 minutes[2]
- Accelerate to 55-60 mph and cruise for 5-10 minutes[2]
- Decelerate to a stop without braking harshly[2]
3. Use Diagnostic Tools
Utilize an OBD-II scanner to check for any error codes or incomplete monitors after completing the drive cycle. Advanced scanners can provide real-time data and freeze frame information, which can be crucial for diagnosing intermittent issues.
4. Analyze Monitor Readiness
Pay close attention to which monitors are not ready:
- If only the oxygen sensor heater monitor is not ready, it may eventually set with more driving[4]
- If multiple monitors are not ready, including the oxygen sensor and catalyst monitors, a weak battery might be the culprit[4]
- If the EVAP monitor is not ready, check the fuel cap and fuel level[4]
5. Consult Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs)
Check for any TSBs related to drive cycle issues for your specific vehicle make and model. Manufacturers often release updates or specific procedures to address known problems.
6. Professional Diagnosis
If you’re unable to resolve the issue, seek help from a professional technician who is familiar with Mode 6 diagnosis and has access to manufacturer-specific diagnostic tools[4].
“If none of the other monitors set, you should also take your vehicle to a shop that truly understands Mode 6 diagnosis.”[4]
Common Solutions for Drive Cycle Issues
Once you’ve diagnosed the problem, consider these potential solutions:
1. Battery Replacement
positive If your battery is more than four years old and monitors are not setting, replacing the battery and re-running the drive cycle may solve the issue[4].
2. Sensor Replacement
Faulty oxygen sensors or mass airflow sensors can prevent successful drive cycle completion. Replacing these components may be necessary if they’re found to be malfunctioning.
3. Software Updates
In some cases, updating the vehicle’s ECU software can resolve drive cycle issues, especially if there are known bugs or calibration problems.
4. Catalytic Converter Inspection
A failing catalytic converter can cause persistent drive cycle issues. Have it inspected and replaced if necessary.
5. EVAP System Repairs
If the EVAP monitor consistently fails to set, check for leaks in the system, including the fuel cap, hoses, and canister.
Preventing Drive Cycle Issues
To minimize the occurrence of drive cycle issues, consider the following preventive measures:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule
- Address check engine lights promptly
- Use high-quality fuel and keep the fuel system clean
- Regularly inspect and replace wear items such as spark plugs and air filters
- Avoid disconnecting the battery unnecessarily
Impact of Drive Cycle Issues on Vehicle Performance and Emissions
Unresolved drive cycle issues can have several negative impacts:
- Increased fuel consumption
- Higher emissions output
- Potential for more severe engine or emissions system damage
- Failed emissions tests and inability to register the vehicle
Addressing drive cycle issues promptly not only ensures compliance with emissions regulations but also maintains optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
FAQs
- How long does a typical drive cycle take to complete?
A typical drive cycle can take anywhere from 20 to 30 minutes under ideal conditions. However, for all monitors to set, it may require multiple drive cycles over several days of normal driving. - Can I complete a drive cycle if my check engine light is on?
Yes, you can complete a drive cycle with the check engine light on. However, if there are active DTCs, some monitors may not run or complete until the underlying issues are resolved. - Will disconnecting the battery reset all monitors?
Yes, disconnecting the battery will clear all DTCs and reset all monitors to “not ready” status. You’ll need to complete a new drive cycle to set the monitors again. - How often should I perform a drive cycle?
For normal vehicle operation, you don’t need to perform specific drive cycles. However, after repairs, code clearing, or battery disconnection, you should complete a drive cycle to ensure all systems are functioning correctly. - Can weather conditions affect drive cycle completion?
Yes, extreme temperatures can affect drive cycle completion. Most vehicle computers won’t run certain tests if the ambient temperature is below freezing or above 90°F (32°C).
Conclusion
Drive cycle issues can be complex and frustrating, but understanding their causes and proper diagnostic procedures can help maintain your vehicle’s performance and emissions compliance. Regular maintenance, prompt attention to warning lights, and following manufacturer-recommended procedures are key to preventing and resolving these issues. If you’re experiencing persistent drive cycle problems, don’t hesitate to seek professional help from a qualified technician who specializes in emissions diagnostics.
Remember, a successfully completed drive cycle not only ensures your vehicle passes emissions tests but also contributes to better fuel economy, reduced emissions, and overall longevity of your vehicle’s critical systems.
Was this page helpful?

Similar Problems in Other Models
Porsche Macan Problems
2007 Ford Fusion Problems
2012 Toyota Sienna Problems
2013 Lexus Gs 350 Problems
2013 Audi A4 Problems
2023 Nissan Rogue Problems
2003 Buick Century Problems
2021 Tahoe Diesel Problems
2023 Kia Sorento Problems
2007 Mercedes E350 Problems
Car News and Reviews
Would you like to take a look at the car news and reviews we have carefully selected and published for you?
2024 Lucid Air Prices Go Down
GM's Big Road Network for Hands-Free Driving
DTC C0561-71 Vacuum Sensor Code on GM, GMC and Chevy
C1201 Code Toyota and Lexus (Causes and Solutions)
Chrysler Auto Start Stop Warning Light (Causes and Solutions)
2024 Ford Mustang GT: Digital Age Meets Classic Power
The 2024 Chevrolet Silverado 2500HD ZR2: An Off-Road Marvel
2024 Chevy Colorado ZR2 Bison: The Ultimate Off-Road Experience
The 2024 Lucid Air Sapphire Track Drive Experience
2024 Subaru Forester Review, Specs, Price, Release Date